Untitled Document
 |
|
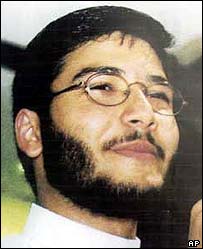
Ahmed Omar Abu Ali's life is ruined by zealots
|
Two presidential assassination plots are making headlines. In one,
Saddam Hussein, the recipient of a presidential assassination attempt, is on
trial for his life because those people involved with the aborted scheme were
held accountable to Iraqi law. In the other, a 25-yeear-old U.S. citizen was
sentenced to 30 years in prison for plotting to kill President Bush.
If the scenarios sound confusing, it is because they are. One president
faces death for being shot at and one student will be in prison for most of
his adult life for threatening another president. All presidents aren’t
created equal.
The more we delve into the particulars, the more bizarre these cases become.
First, Saddam Hussein was in a motorcade in 1982 and the plotters began shooting.
In the end, Saddam was not hit, but many people were rounded up and sent for
questioning. Those who were part of the attack were eventually put on trial
and sentenced to death. Some of the participants escaped and fled to Iran. One,
in particular, is now the Prime Minister of Iraq.
In Saddam’s case, real bullets were fired by people trying to assassinate
him. And, this was during wartime as his country was fighting a bloody conflict
against Iran.
Today, Saddam sits in a prison awaiting judgement for being the president of
a country in which the justice system gave the death penalty for the assassination
attempt. His trial so far is a farce, a "kangaroo court." This term
is used to describe court proceedings that aren’t fair and the outcome
is already predetermined. It is ironic that the term "kangaroo court"
first came into use in the U.S. state of Texas, Bush’s home turf. According
to www.wordorigins.org:
Interestingly, the term kangaroo court, meaning a criminal proceeding that
is conducted for show and where the defendant is inevitably going to be found
guilty, is not of Australian origin. The earliest use of the term was recorded
in Texas, of all places, circa 1850. The term Kangaroo court was unknown in
Australia until it was introduced there from America. No one knows how this
term arose, but it is usually assumed to be in reference to how the defendant
will be bounced from the court to the gallows. Lighter suggests that the term
may have arisen from the way a kangaroo court defies the law, just as the
kangaroo's appearance seems to defy the laws of nature.
Let’s take a look at the case of Ahmed Omar Abu Ali. He is a 25-year-old
U.S. citizen who was studying in Saudi Arabia. Last week, he was sentenced to
30 years in prison for plotting to kill Bush.
The only "proof" used to convict him was a confession he signed in
Saudi Arabia. Once he left the enlightened kingdom and returned to the U.S.,
he alleged that his signature was only given because he was severely tortured.
He recanted his confession.
Not one piece of paper, or a weapon, or a phone conversation, or anything else
was found to implicate Ali in an assassination plot; a plot that never existed.
Ali’s life is ruined for allegedly threatening one president, while Saddam
faces the gallows for being a president who was shot at.
There are many implications about the illegalities of Ali’s case. I found
an article that is comprehensive that discusses Ali’s legal plight. It
came from a legal, not political, source (www.FindLaw.com) used by legal professionals.
It was written a few days before Ali was sentenced.
The Strange Case of Ahmed Omar Abu Ali:
Troubling Questions about the Government's Motives and Tactics
By ELAINE CASSEL
Monday, Mar. 07, 2005
The case is far from as open-and-shut as the FBI might suggest. Indeed, a number
of aspects of the prosecution are deeply troubling.
The Early History of Abu Ali's Case: The Government Reverses Itself
At the end of the 2003 academic year at the Saudi university he was attending,
Abu Ali failed to return home to the U.S. As a result, his family - Jordan-born,
naturalized U.S. citizens living in Northern Virginia where I practice - contacted
me to see if I could help.
In August 2004, attorneys filed suit in the U.S. District Court of the District
of Columbia, on behalf of Abu Ali's parents, in order to obtain his release.
Among the attorneys was renowned constitutional rights scholar and Georgetown
University law professor David Cole.
The day the suit was filed, the State Department - which had previously refused
to provide information to Abu Ali's parents - notified them that their son would
be charged with crimes of terrorism in Saudi Arabia. But that never happened.
Instead, the question of whether Abu Ali could be returned to the U.S. was litigated.
Before U.S. District Judge John Bates, the government took the position that
Abu Ali was far too dangerous to ever be returned to the United States, and
that the reason was so serious that it could not be disclosed even to the family's
attorneys. In other words, the government sought to proceed on secret evidence.
Then, the government reversed itself dramatically. It transported Abu Ali to
the United States itself - thus mooting the question before Judge Bates of whether
the government could proceed upon secret evidence to block his return.
In 2004, when Abu Ali's parents had been begging the U.S. government to intervene,
it had refused - claiming it was up to the Saudis whether he was released. With
his return, however, it began to seem evident that the Saudis had been holding
Abu Ali with U.S. consent - indeed, even at the U.S.'s behest. It now appears
that FBI agents had the Saudis remove Abu Ali from his university class and
take him to a Saudi facility for questioning in the summer of 2003.
It also became apparent that the U.S. could, all the time, have ensured Abu
Ali's return to the U.S. whenever it felt like it. After all, federal prosecutors
had, during this time, extradited from Saudi Arabia to Alexandria another man
in Saudi custody who was alleged to be (and acquitted of being) a terrorist
and involved in the case of the Alexandria 11.
Apparently, however, the U.S. had taken advantage of this U.S. citizen's choice
to attend school abroad, to make sure he was held in prison there - where torture
would be permitted, and counsel would not be provided. Indeed, unidentified
sources have been quoted in the Washington Post and New York Times as saying
that the government certainly would have preferred to have left Abu Ali in Saudi
Arabia.
It was only Judge Bates's interest in Abu Ali's case that changed the government's
mind. Laudably, Bates was concerned - as we all should be -- about the potentially
indefinite imprisonment of a U.S. citizen, with the U.S.'s consent, in a foreign
prison where due process is ignored and torture is common.
With Judge Bates perhaps unwilling to proceed against Abu Ali in absentia,
the government felt it had to bring him home. To do so, they had to charge him
with something--something that would at least sound serious, even if the underlying
indictment (as I will explain below) fell far short of the media headline.
The Government Argues Abu Ali Ought to Be "Presumed Dangerous"
Abu Ali was arraigned, as noted above, on February 22. On February 24, a hearing
on whether he would be released prior to trial was to occur. But the government
managed to delay that hearing. It did so by arguing that the usual standard
for pre-trial release should not apply.
Typically, in a criminal case, to block a defendant's release on bail, the
government must prove the defendant's dangerousness or his likelihood of fleeing.
But here, the government took the position that the defendant, Abu Ali, had
the burden of proving to the court that he would not be a danger to national
security, before being released on bail. It did so based on 2004 federal legislation
stating that people charged with terrorism-related crimes were presumed to be
too dangerous to be released unless they proved otherwise.
The
Eighth Amendment requires that "excessive" bail shall not be required,
and constitutional due process applies to federal pre-trial criminal proceedings.
Moreover, two centuries of law have mandated that the government has to prove
that a defendant would be a flight risk or danger to the community if not released
on the condition he pay bail and/or comply with other requirements.
More fundamentally, our system depends on the idea that we jail people for
criminal conduct, not merely the government's insistence that they are "dangerous."
In order to honor this principle, we have made sure that we have no common law
crimes - only those specifically defined by statute.
The importance of this principle simply cannot be overstated. Without it, governments
could simply lock up unpopular minorities, political opponents, and political
dissidents - and as South American and Eastern European history shows us, they
have.
The Government Relies on a U.S. Citizen's Saudi-Prison Confession
At the hearing on the bail motion, an FBI agent testified that Abu Ali had
confessed to Saudi officials that he associated with persons involved with al-Qaeda,
received things of value from them, and talked with one or more of them about
how to assassinate President Bush, whether by car bomb or shooting. (These persons
are named in the indictment as unindicted co-conspirators.) The government also
claims to have a videotape of this confession.
Abu Ali's attorneys argued that if Abu Ali indeed confessed, he did so under
extreme conditions of confinement - conditions that included torture. Confessions
under such circumstances are not only deeply inhumane; they are also notoriously
unreliable.
They also pointed out that Abu Ali had repeatedly been denied the right to
an attorney. Abu Ali's parents had asked the U.S. consulate in Saudi Arabia
-- who had infrequently sent an employee to visit Abu Ali in prison -- to provide
their son with an attorney. They were told the Saudis would not allow it. Accordingly,
no attorney ever met with Abu Ali while he was incarcerated and doubtless tortured
in Saudi Arabia.
Hopefully, the Alexandria judge will exclude the confession from evidence to
be heard at Abu Ali's trial. He could do so on the ground that Abu Ali was,
in effect, in U.S. custody - and thus, his Fifth Amendment rights were violated.
Or, the judge could do so on a simpler ground: that the prejudicial effect of
coerced confessions outweighs their probative value. (Federal trial judges may
make this prejudicial effect/probative value balance for any piece of evidence
the government seeks to offer.)
The Government Searches Abu Ali's Parents Home pursuant to the USA
PATRIOT
The government also admitted at the bail hearing that it had secretly raided
Abu Ali's parents' home in 2003 - apparently pursuant to the USA PATRIOT Act
-- and found what it deemed to be "radical" Islamic writings. It also
found a gun magazine - hardly unusual for Virginia.
This search had occurred incident to the prosecution of the "Alexandria
11." I have written about this group in an
earlier column. Abu Ali and his parents were certainly not among them -
but because they lived in the same community, apparently they fell under suspicion
anyway.
In Abu Ali's case, the government was able to use two arguably unconstitutional
laws--the USA PATRIOT Act, which allows secret, warrantless searches, and the
law the government invoked, which allows pre-trial dangerousness to be presumed.
Through the combination of these laws, it was able to search secretly for supposed
evidence of dangerousness, craft an overblown indictment, flood the media with
dramatic press releases, and then dare the defendant to prove his innocence.
The Government's Indictment: Where's the Conspiracy?
When the
indictment was made available to the public, it raised an even larger question
about the entire prosecution. Nowhere in the indictment is Abu Ali tied to any
terrorist event or action. So what is his crime?
Plainly, there was not enough support for a charge of conspiracy to assassinate
President Bush. Conspiracy requires an agreement, and an overt
act in furtherance of the agreement. Nothing in the indictment suggests
that Abu Ali either agreed to attempt to assassinate Bush, or took any action
as a step to doing so.
So, instead, the indictment simply charges Ali with having "associated"
with alleged terrorists. Specifically, it claims that he talked about wanting
to kill Bush with these persons, and that he received money from one or more
of them - for what purpose, it is unclear.
The very reason that the law of conspiracy requires an agreement and an overt
act is to prevent prosecutions like this one - based on alleged, vague discussions
that supposedly took place, but were never acted upon.
What Abu Ali's Case Signifies for America and the Rule of Law
The next development in the Abu Ali case may be a plea agreement. The government's
case is obviously weak, and its evidence depends on conduct that many view as
unconstitutional - even appalling.
The government will be in the same bind it is in the Zacarias Moussaoui case.
There, it has successfully argued that it cannot produce witnesses because they
are of such high intelligence value to the government that they have to be kept
in secret. It has also argued that given that this is the case, the defendant
can't subpoena these witnesses because their appearance, pursuant to Moussaoui's
Sixth Amendment right to face his accusers, would be a grave threat to national
security.
If prosecutors offer Abu Ali a deal and he refuses, he will sit in jail for
years as the case winds it way through appeal after appeal, as his occurred
in the Moussaoui saga.
If Abu Ali pleads guilty, he will no doubt be placed under a gag order, like
that imposed on John Walker Lindh. It will require, most certainly, that he
never speak in public about anything related to the court case, or about what
happened to him while he was in Saudi custody.
The plea agreement may also require that Abu Ali return to Saudi Arabia - as
the agreement the government entered into with U.S. citizen Yaser Hamdi did
- even though that means he will be separated from his family. (The agreement
followed upon Hamdi's victory
in his Supreme Court case.)
Speaking of his family, Abu Ali's family have not been able to visit him since
his return because they refused to agree to the government's rules: An FBI agent
had to be present during the visits, all their communications had to be in English,
and they could make no comment to anyone, including the press of course, about
any aspect of their visit. Is it any wonder they refused?
To add insult to injury, the family has been ordered not to "communicate"
with their son in the courtroom. Did this extend to a smile, a loving glance,
they asked the magistrate?
If Abu Ali's case does end in a plea agreement - or, worse, in a precedent
blessing this prosecution as constitutional - Americans' rights will have been
very significantly diminished.
Such a result will mean that this nightmare is viewed as an entirely legal
reality: The U.S. can work with a foreign government to arrest and imprison
a U.S. citizen and torture him. It can allow the imprisonment to go on indefinitely;
Abu Ali's took over twenty months.
Citizens of U.S. allies, too, should beware: Canadian citizen Maher Arar was
kidnapped by CIA operatives from New York's Kennedy airport, and taken to Syria
for "questioning." There he remained for a year, until Syria got annoyed
with the United States and returned Arar to Canada.
Then, if the U.S. (or allied country) citizen confesses under torture - and
virtually everyone does, even if the confession is a lie - the U.S. may try
to use the confession against him in a U.S. court, as well in a foreign court.
(We don't know why the intended Saudi prosecution of Abu Ali got sidetracked.
Could it be because the Saudis thought, as did the Syrians about Maher Arar,
that no crime had been committed?)
But, readers may object, what if the U.S. really thinks Abu Ali is a terrorist?
The answer is that the U.S. can still protect its citizens from him - consistent
with the Constitution.
How? The U.S. could have promptly extradited him from Saudi Arabia to face
charges here. Once he was here, it could have honored his right, as a U.S. citizen,
to an attorney, a speedy trial, and a right to pretrial release unless the government
proved that he was a danger or a flight risk.
This is not too much to ask. And it is what the Constitution requires.

